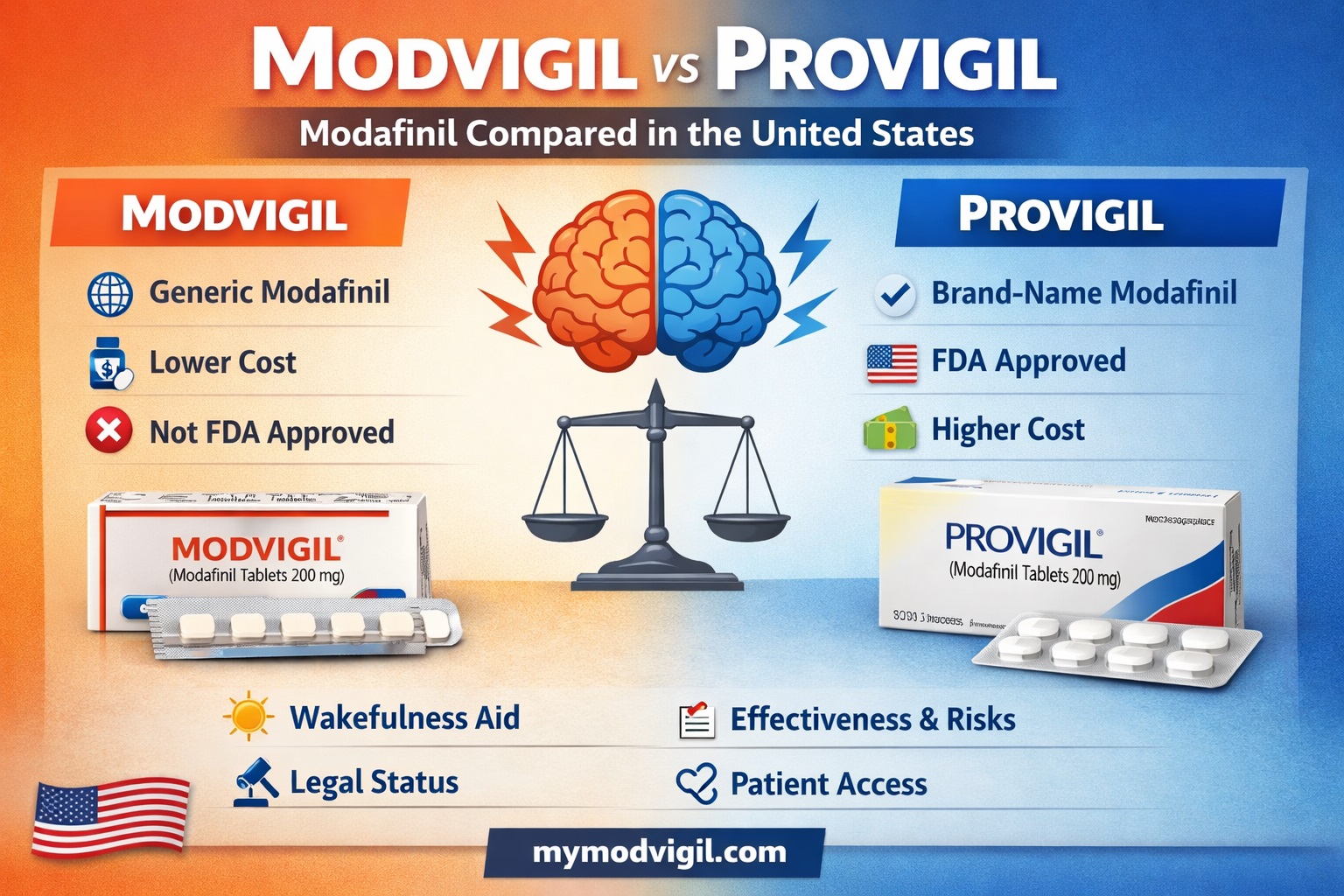
For patients researching treatments for chronic sleepiness, Modvigil and Provigil often appear side by side. Both are associated with alertness, focus, and long waking hours. Yet the similarities can be misleading. Although the two drugs share the same active compound—modafinil—their clinical, regulatory, and practical profiles differ in meaningful ways. Understanding those differences helps patients move beyond marketing claims and toward informed decisions. This article unpacks Modvigil vs Provigil with a clinician’s eye and a journalist’s restraint. The goal is clarity, not promotion, grounded in how these medications are actually used and regulated in the United States. Additional background resources are available throughout at mymodvigil.com.
Definitions and Core Mechanisms
What Is Provigil?
Provigil is the original brand-name formulation of modafinil, approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in 1998. It was developed specifically to treat narcolepsy and later approved for shift work sleep disorder and obstructive sleep apnea–related sleepiness.
As a branded medication, Provigil went through extensive clinical trials and long-term post-marketing surveillance. These processes established its dosing standards, safety warnings, and prescribing norms.
What Is Modvigil?
Modvigil is a generic modafinil product manufactured primarily outside the United States. It contains the same active molecule but is not FDA-approved for domestic sale.
Patients often encounter Modvigil while researching alternatives for persistent fatigue or excessive daytime sleepiness. This context is explored further in Modvigil and Excessive Daytime Sleepiness: Legal, Regulatory, and Clinical Context.
What Are Eugeroics?
Modafinil belongs to a drug class known as eugeroics, or wake-promoting agents. Unlike classical stimulants, eugeroics aim to enhance alertness without producing intense dopamine surges or euphoric effects.
This distinction matters clinically. It underlies many discussions about the difference between nootropics and eugeroics, especially when patients compare modafinil with ADHD medications. A clinical comparison is available in Modvigil vs Adderall for Sleep Disorders: Legal, Regulatory, and Clinical Context.
How Modafinil Works in the Brain
Modafinil’s mechanism of action is best described as broad and modulatory rather than forceful. It increases wakefulness by influencing dopamine transporters while also interacting with norepinephrine, histamine, and orexin systems.
Importantly, it does not trigger the same rapid dopamine spikes seen with amphetamines. This helps explain why many patients report sustained alertness without the “crash” associated with traditional stimulants.
A more detailed neurobiological explanation is provided in How Modvigil Works in the Brain.
Off-Label Use and Growing Public Interest
Although Provigil is FDA-approved for specific sleep disorders, modafinil is frequently prescribed off-label. In clinical settings, physicians often observe its use for fatigue related to depression, multiple sclerosis, or demanding work schedules.
Off-label prescribing is legal in the United States, but it requires careful clinical judgment. Importantly, neither Modvigil nor Provigil is approved as a cognitive enhancer, despite popular narratives online.
This gap between medical intent and public perception fuels confusion about modafinil legal status and appropriate use.
Clinical Insights — What Physicians Notice Over Time
From a clinician’s standpoint, Provigil offers predictability. Its dosing, absorption, and adverse-event profile are well documented through years of FDA oversight.
Modvigil introduces more uncertainty. While many patients report comparable effects, physicians cannot easily verify manufacturing standards or batch consistency. This does not imply inferiority—but it does complicate risk assessment.
In practice, clinicians tend to favor FDA-approved products when long-term treatment or comorbid conditions are involved.
Risks and Side Effects
Common Effects Shared by Both
Because both medications rely on modafinil, their core side-effect profiles overlap:
- Headache
- Nausea
- Reduced appetite
- Insomnia or restlessness
These effects are usually dose-related and often improve with adjustment.
Rare but Serious Risks
Modafinil has been associated with rare but severe dermatologic reactions, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome. This risk prompted strong warnings in FDA labeling and underscores the need for medical supervision.
Differences in tolerability between products may stem from inactive ingredients rather than the drug itself. A breakdown of formulation components is available in What Are the Ingredients of Modvigil?.
Modvigil vs Provigil Cost, Access, and Real-World Trade-Offs
One of the most visible differences between Modvigil and Provigil is cost. Provigil remains expensive in U.S. pharmacies, even as generic options exist.
Modvigil’s lower price point often drives patient interest, especially among those without insurance. Pricing considerations are discussed in Modvigil Price Over the Counter: What Patients Need to Know.
However, affordability must be balanced against legal clarity and quality assurance.
Comparisons and Alternatives
Modvigil vs Artvigil
Artvigil contains armodafinil, a related compound with a longer half-life and sometimes smoother wakefulness. Comparative differences are outlined in Overview: Modvigil vs Artvigil.
When Alternatives Are Considered
Physicians may explore alternatives when patients experience side effects, insufficient benefit, or regulatory barriers. These decisions depend heavily on diagnosis, lifestyle, and comorbid conditions.
Regulatory Notes — Why Approval Status Matters
Provigil is FDA-approved and classified as a Schedule IV controlled substance in the United States. Its manufacturing, labeling, and post-market safety reporting are tightly regulated.
Modvigil, while chemically similar, does not carry FDA approval for U.S. distribution. This distinction affects prescribing practices, patient protections, and legal risk.
Authoritative guidance on modafinil regulation can be found through:
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
FDA Modafinil (Provigil) Prescribing Information and Safety Labeling - National Institutes of Health (NIH)
NIH – Modafinil: Pharmacology, Mechanism, and Clinical Use - World Health Organization (WHO)
WHO ATC Classification System: Modafinil (N06BA07)
Conclusion — One Molecule, Two Frameworks
Modvigil and Provigil share a pharmacological foundation but exist in different medical and regulatory ecosystems. One is embedded in U.S. clinical infrastructure; the other operates largely outside it.
For patients, the choice is rarely theoretical. It reflects cost, trust, legality, and access to medical oversight. Understanding those layers matters as much as understanding modafinil itself.
Medical Disclaimer
This article is for informational purposes only and not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider.